ipsrdbs1. Introduction to Basic Statistics2. Getting Started with R3. Introduction to Probability4. Conditional Probability and Independence5. Random Variables and Their Probability Distributions6. Standard Discrete Distributions7. Standard Continuous Distributions8. Joint Distributions and the CLT9. Introduction to Statistical Inference10. Methods of Point Estimation11. Interval Estimation12. Hypothesis Testing13. Generating Functions14. Transformation and Transformed Distributions15. Multivariate Distributions16. Convergence of Estimators17. Simple Linear Regression Model18. Multiple Linear Regression Model19. Analysis of VarianceResourcesPdfCorrections
ipsrdbs1. Introduction to Basic Statistics2. Getting Started with R3. Introduction to Probability4. Conditional Probability and Independence5. Random Variables and Their Probability Distributions6. Standard Discrete Distributions7. Standard Continuous Distributions8. Joint Distributions and the CLT9. Introduction to Statistical Inference10. Methods of Point Estimation11. Interval Estimation12. Hypothesis Testing13. Generating Functions14. Transformation and Transformed Distributions15. Multivariate Distributions16. Convergence of Estimators17. Simple Linear Regression Model18. Multiple Linear Regression Model19. Analysis of VarianceResourcesPdfCorrections
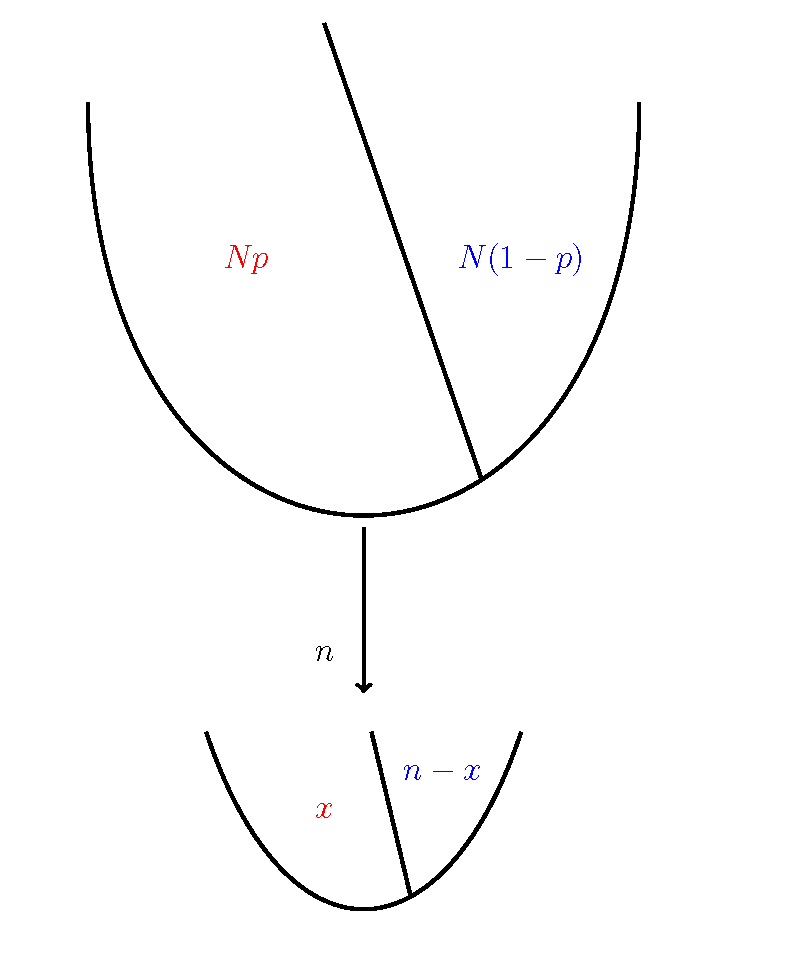
3. Introduction to Probability
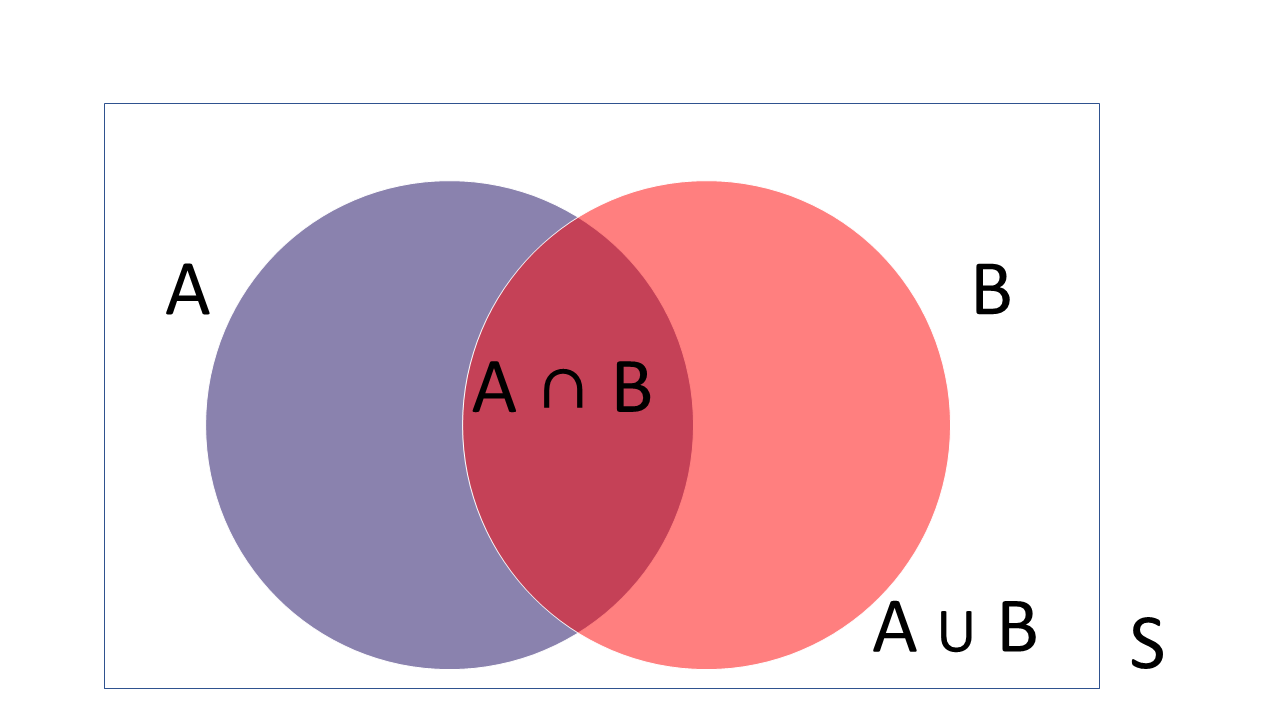
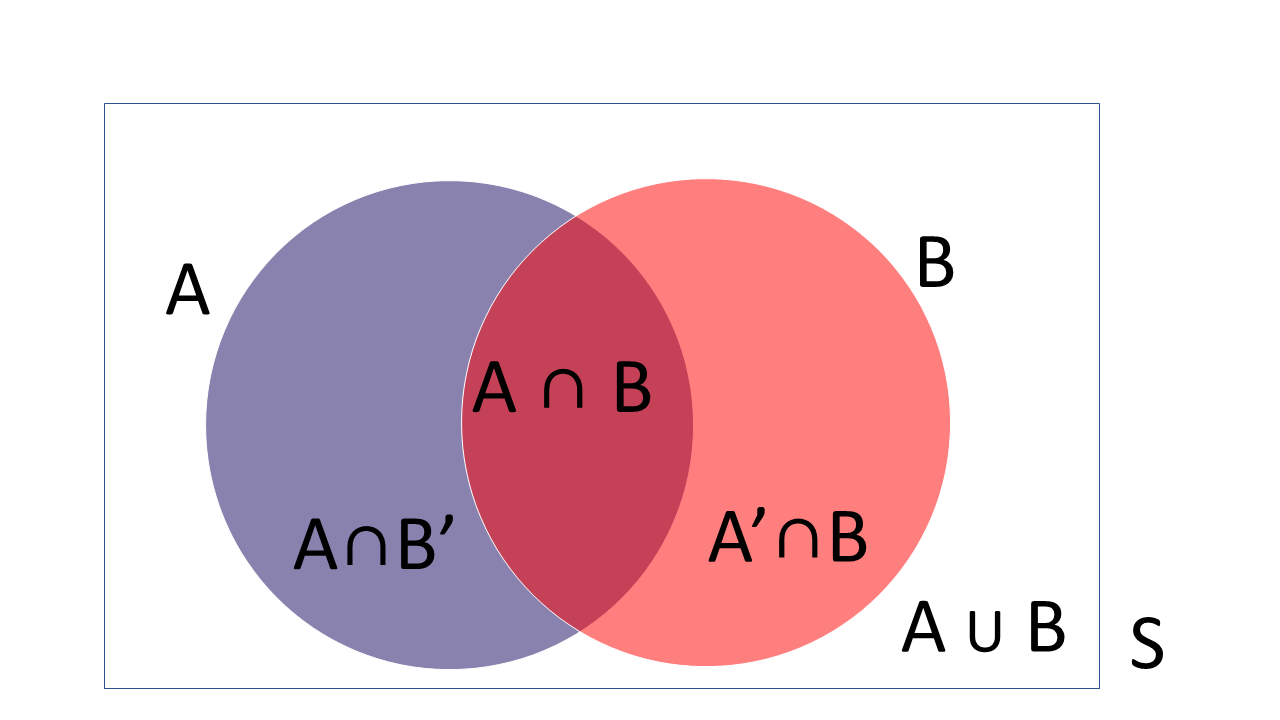
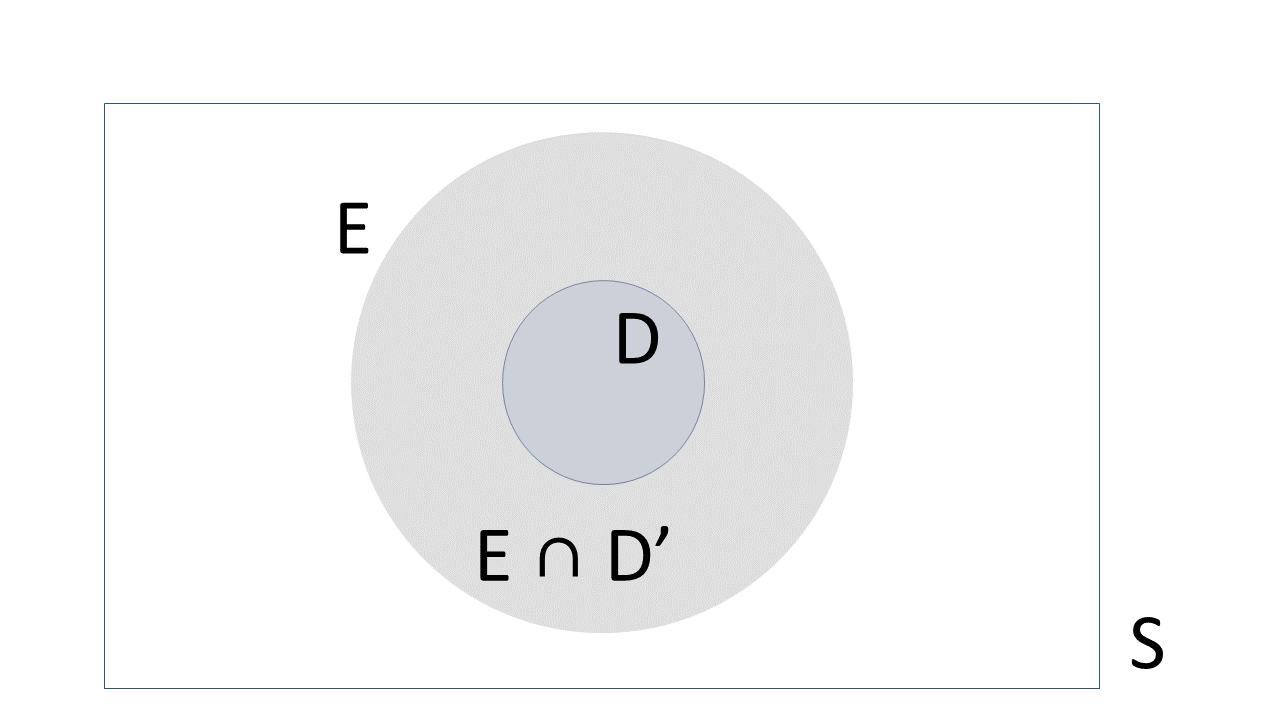
The basic concepts of probability are introduced in this chapter. Elementary methods of counting, the number of permutations and the number of combinations are introduced and illustrated. Elementary methods for calculating probabilities are discussed and the general urn problem in probability is defined.